How Do Living Walls Improve Building Efficiency?
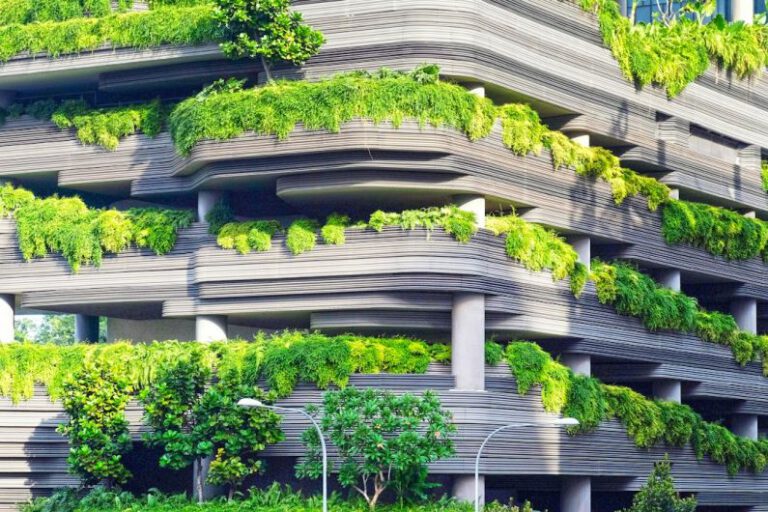
Living walls have been gaining popularity in the realm of sustainable architecture as a means to enhance both the aesthetic appeal and efficiency of buildings. These vertical gardens, also known as green walls, are composed of living plants that are integrated into the exterior or interior of a structure. Their ability to improve building efficiency goes beyond just visual enhancement, as they offer a multitude of benefits that contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly environment. From reducing energy consumption to improving air quality, living walls have emerged as a valuable asset in modern building design.
Enhanced Insulation and Temperature Regulation
One of the key ways in which living walls improve building efficiency is through enhanced insulation and temperature regulation. By acting as a natural barrier, the layer of vegetation on a living wall helps to regulate the temperature inside a building by providing insulation against heat in the summer and cold in the winter. This natural insulation reduces the need for excessive heating or cooling, thereby decreasing energy consumption and lowering utility costs.
Improved Air Quality and Health Benefits
Living walls are not only visually appealing but also serve as natural air purifiers, contributing to improved indoor air quality. The plants on a living wall help to filter out pollutants and toxins from the air, creating a healthier and more breathable environment for building occupants. This enhanced air quality can lead to a range of health benefits, such as reduced respiratory issues, increased productivity, and overall well-being.
Noise Reduction and Acoustic Control
In addition to their thermal and air quality benefits, living walls also offer acoustic benefits by reducing noise pollution. The vegetation on a living wall acts as a sound buffer, absorbing and dampening noise from the surrounding environment. This can be particularly advantageous in urban areas or busy commercial spaces where noise levels can be a concern. By incorporating living walls, buildings can create a more peaceful and tranquil indoor environment for occupants.
Biodiversity and Ecological Benefits
Another significant advantage of living walls is their contribution to biodiversity and ecological sustainability. By providing a habitat for various plant species, living walls support biodiversity and help promote a healthier ecosystem within urban environments. This green infrastructure plays a role in mitigating the urban heat island effect, enhancing urban biodiversity, and promoting ecological balance in built-up areas.
Aesthetic Appeal and Biophilic Design
Beyond their functional benefits, living walls also offer aesthetic value and contribute to biophilic design principles. The lush greenery of a living wall adds a touch of nature to the built environment, creating a visually striking and harmonious space. This integration of nature into architecture not only enhances the overall aesthetic appeal of a building but also fosters a connection to the natural world, promoting well-being and reducing stress among occupants.
Maintenance and Sustainability Considerations
While the benefits of living walls are numerous, it is essential to consider maintenance and sustainability aspects when incorporating them into building design. Proper irrigation systems, plant selection, and maintenance protocols are crucial to ensuring the longevity and health of a living wall. Additionally, selecting native plant species and utilizing sustainable practices in the construction and upkeep of living walls are essential for maximizing their environmental benefits.
In conclusion, living walls have emerged as a versatile and effective tool for improving building efficiency and sustainability. From enhancing insulation and temperature regulation to improving air quality and promoting biodiversity, the benefits of living walls extend beyond mere aesthetics. By integrating these vertical gardens into building design, architects and designers can create healthier, more sustainable, and visually appealing spaces that benefit both occupants and the environment.